Did you know? Starting in the Washington release, ServiceNow's Rhino engine now natively supports JavaScript Arrow Functions!
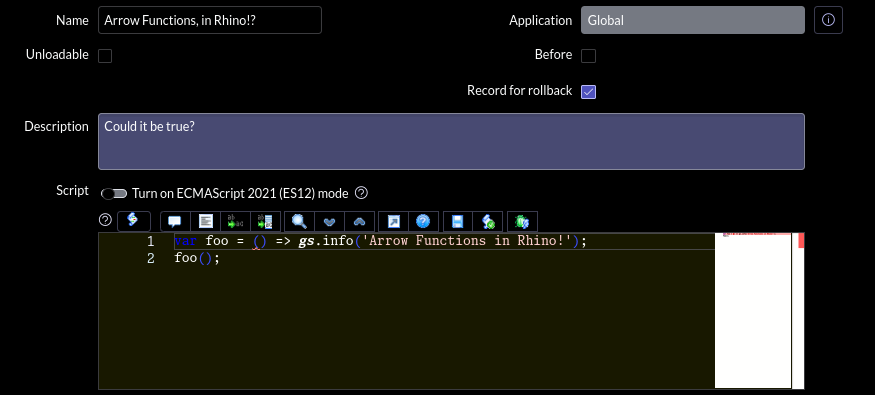
It works everywhere server-side code runs. Even in the Global scope without using the new "Turn on ECMAScript 2021 (ES12) mode" button.
How can this be??
Those of you following recent ServiceNow releases have probably already (correctly) intuited that this new development must be somehow related to the recent introduction of the new "ES12" JavaScript Mode. This is true... to an extent.
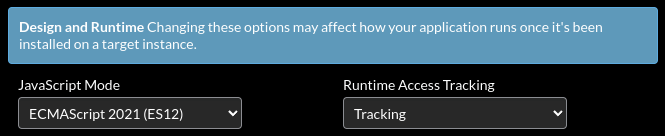
Internally, ServiceNow uses an ancient JavaScript engine known as Rhino. Rhino doesn't support most ES12 features, yet ServiceNow still somehow supports ES12... How is ServiceNow pulling off that magic trick? In short: Transpilation. Transpilers automatically convert modern code into legacy-compatible code – ServiceNow has a built-in auto-transpiler which automatically converts code wherever "ES12" mode has been enabled.
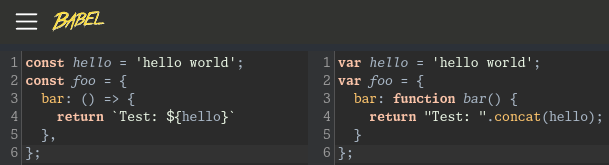
So, is that what's going on here? Did ServiceNow accidentally turn on their magic transpilation step everywhere and somehow never notice? Nope! That's definitely not the case because many other ES12 JavaScript features available remain unusable.
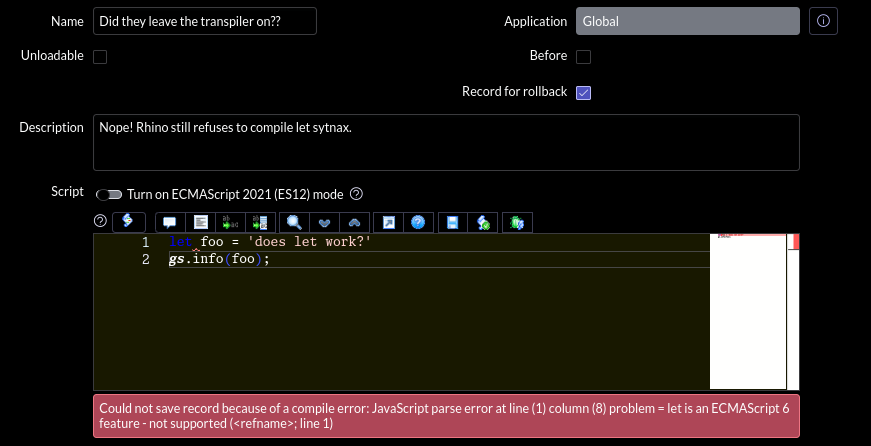
So... what's going on here, if not transpilation? The answer is actually rather simple: ServiceNow's version of Rhino has been upgraded to a newer release – first 1.7.12 in Washington, then 1.7.14 in Xanadu.
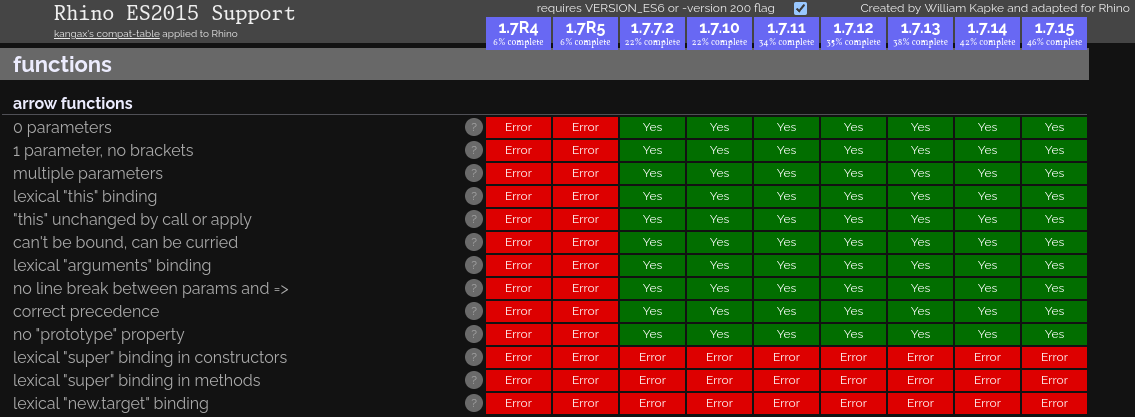
We can prove this by checking if Array.prototype.includes is available. This is a newer Array method which only gained support starting in Rhino version 1.7.12.
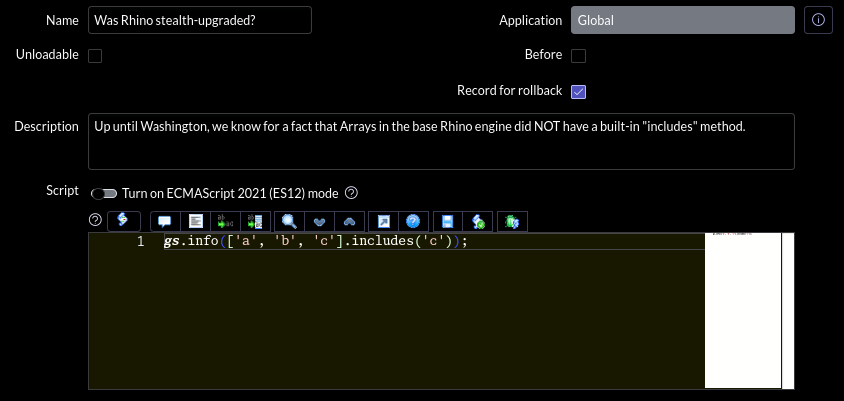
The proof is in the pudding. As you can see below: Rhino has gained native support for many new language features which were previously impossible!
array.indexOf('foo') !== -1 begone!This long-overdue engine update can be chalked up to a happy side-effect of ServiceNow's ongoing work on the new "ES12" JavaScript transpilation mode:
More engine features => Less transpilation => Better performance & accuracy
What's The Catch?
The catch is that Rhino is still an old engine without full ES12 support. Even if some new features have become available, >50% of all modern JavaScript features are still unavailable to Rhino. In other words: most modern features are still locked behind transpilation (i.e. "ES12" mode), Rhino upgrade notwithstanding.
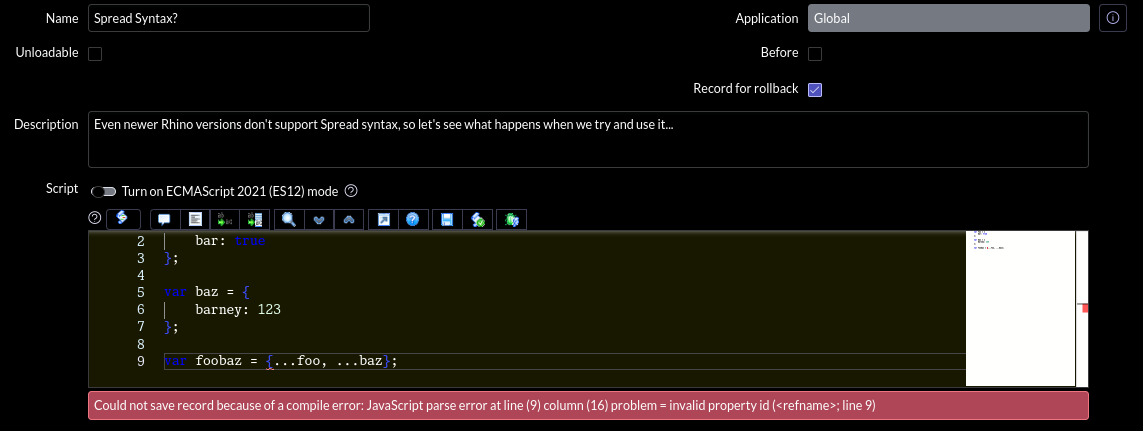
How do I know what's newly available in my Instance?
Our research indicates two recent upgrades to the Rhino engine:
- Washington: Rhino 1.7.12
- Xanadu: Rhino 1.7.14
Consulting this table, search for any features which were red in 1.7R5 and now green in your instance's Rhino version (see directly above). Easy peasy!
Not so easy? Well, dear reader, this must be your lucky day because as a special gift just for you I've already compiled a list and snuck it in right below 😁
- Method Shorthand
{ foo(){ return 'foo!'; } }vs{ foo: function(){ return 'foo!'; } } - Arrow Functions
(foo) => foo.explode() - Template Literals (Xanadu+)
`One plus one equals ${ 1 + 1 }. Two plus two equals ${ 2 + 2 }` - Array.from
Array.from('foo') // ['f', 'o', 'o'] - Array.of
Array.of(1, 2, 3) // [1, 2, 3] - Array.prototype.copyWithin
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5].copyWithin(2, 0, 2) // [0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 5] - Array.prototype.includes
[1, 2, 3].includes(2) // true - Array.prototype.find
[1, 2, 3, 4].find((x) => x > 2) // 3 - Array.prototype.findIndex
['a', 'b', 'c'].find((x) => x.startsWith('b')) // 1 - Array.prototype.fill
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6].fill('X', 2, 4) // [1, 2, 'X', 'X', 'X', 6] - Math.cbrt
Math.cbrt(64) // 4 (cube root) - Math.clz32
Math.clz32(1) // 31 (number of leading zeroes in 32-bit binary) - Math.cosh
Math.cosh(2) // 3.7621956910836314 (hyperbolic Math.cos) - Math.acosh
Math.acosh(2) // 1.3169578969248166 (hyperbolic Math.acos) - Math.expm1
Math.expm1(1) // 1.718281828459045 (Math.exp(X) - 1) - Math.hypot
Math.hypot(3, 4) // 5 (hypotenuse) - Math.imul
Math.imul(3, 3.5) // 9 (integer multiplication) - Math.log10
Math.log10(1000) // 3 (base-10 logarithm) - Math.log2
Math.log2(8) // 3 (base-2 logarithm) - Math.sign
Math.sign(-10) // -1 - Math.sinh
Math.sinh(2) // 3.626860407847019 (hyperbolic Math.sin) - Math.asinh
Math.asinh(2) // 1.4436354751788103 (hyperbolic Math.asin) - Math.tanh
Math.tanh(1) // 0.7615941559557649 (hyperbolic Math.tan) - Math.atanh
Math.atanh(0.5) // 0.549306144334055 (hyperbolic Math.atan) - Math.fround
Math.fround(5.05) // 5.050000190734863 (round to single precision) - Math.trunc
Math.trunc (9.99) // 9 - Number.EPSILON (Xanadu+)
Number.EPSILON // 2.220446049250313e-16 - Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER
Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER // 9007199254740991 - Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER
Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER // -9007199254740991 - Number.isFinite
Number.isFinite(Infinity) // false - Number.isInteger
Number.isInteger(0.5) // false - Number.isSafeInteger
Number.isSafeInteger(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER + 1) // false - Number.isNaN
Number.isNaN(NaN) // trueNumber.isNaN('foo') // false (unlike global.isNaN) - Number.parseFloat
Number.parseFloat('123.456') // 123.456 (same as global.parseFloat) - Number.parseInt
Number.parseFloat('123') // 123 (same as global.parseInt) - Object.assign
var foo = { a: 1, b: 2 };
Object.assign(foo, { c: 3 }); // foo becomes { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 }; - Object.is
Object.is(-0, +0) // false, unlike a === check - String.fromCodePoint (Xanadu+)
String.fromCodePoint(9733) // '★' - String.raw (Xanadu+)
String.raw`¯\_(ツ)_/¯` // '¯\_(ツ)_/¯' (No escape necessary!) - String.prototype.codePointAt
'☃★♲'.codePointAt(1) // 9733 - String.prototype.includes
'foobar'.includes('oba') // true - String.prototype.normalize
'\u00F1'.normalize('NFC') === '\u006E\u0303'.normalize('NFC') // true - String.prototype.padStart
'12345'.padStart(8, '0') // '00012345' - String.prototype.padEnd
'12345'.padEnd(8, '0') // '12345000' - String.prototype.repeat
'the end is never '.repeat(2) // 'the end is never the end is never' - String.prototype.startsWith
'foobar'.startsWith('foo') // true - String.prototype.endsWith
'foobar'.startsWith('bar') // true
